By your side at every stage
Products with high technological added value to satisfy the specifications of the players in the energy market

Chauvin Arnoux Energy, part of the Chauvin Arnoux Group, proposes its technological expertise to all the people involved in the energy production, transmission and distribution sectors in order to offer them a range of accurate, reliable and long-lasting products and systems.
Nuclear, thermal and hydroelectric power plants and wind or solar farms: Chauvin Arnoux Energy covers the specific and standardized measurement and metering requirements of energy production companies with an offering of products operating in very severe environments:
• Automation relays
• Measurement transducers
• Analogue and digital panel meters
• Recorders
• Power monitors
For energy transmission and distribution networks continuously operated, maintained and developed, Chauvin Arnoux Energy proposes high-technology equipment:
• Measurement transducers
• Tariff meters
• Low-voltage current transformers for tariff metering
• Power monitors
• Network analyzers
• Automation relays
Network balance and energy quality
The multiple, diverse locations and methods used for energy production are forcing historical energy producers to make sure that their network is suitably balanced and maintain the quality of the energy transmitted. Part of the energy produced is intermittent and difficult or impossible to control, although the electrical networks were originally designed to transmit electricity produced in a centralized way in one direction only, from the producer to the consumer. Injection of such intermittent production now means that electrical networks have to operate in both directions. This is why it is increasingly important for network managers to measure at all points in installations in order to maintain the right balance between production and consumption while guaranteeing the stability, reliability and quality of the power supply and service for everyone.
Chauvin Arnoux Energy, part of the Chauvin Arnoux Group, proposes to meet this challenge with network managers in order to manage the electrical system proactively in the presence of distributed, unpredictable energy sources by offering reliable, long-term solutions.References
Nuclear plants:
CNPE EDF (France)
GUANGDONG NPP (China)
LINGAO NPP (China)
KHNP (Korea)
KOEBERG NPP (South Africa)
Transport & Distribution:
RTE (France)
ERDF (France)
CIE (Côte d'Ivoire)
EDELNOR (Peru)
EDESUR and TRANSENER (Argentina)
EDL (Lebanon)
ELECTRABEL (Belgium)
ENEL (Italy)
SEC (Saudi Arabia)
NEK (Bulgaria)
ONE (Morocco)
PLN (Indonesia)
SONELGAZ (Algeria)
STEG (Tunisia)
SONABEL (Burkina Faso)
SENELEC (Senegal)
TNB (Malaysia)
UTE (Uruguay)
K3 qualification
A demanding approach
To fulfil the safety requirements stipulated by customers in the nuclear sector, Chauvin Arnoux Energy is committed to an approach which is specific to this cutting-edge industry, with a K3-qualified offering.
This EDF qualification for use in nuclear power plants obliges equipment installed outside the containment building to be capable of operating under seismic stress in normal environmental conditions. This capability is demonstrated by a qualification programme specific to each type of equipment.
Chauvin Arnoux Energy K3-qualified products
• T82 measurement transducers
• RE3000N and OK-B 184 automation relays
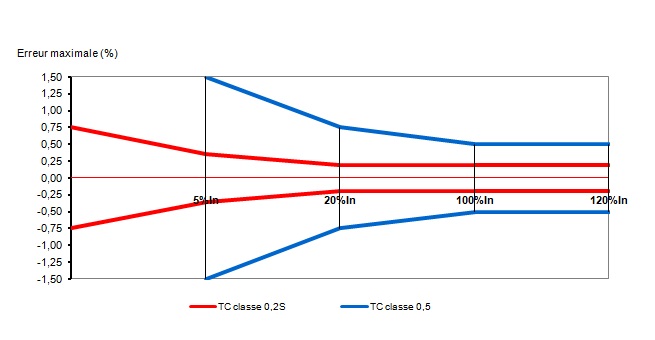
Why install Class 0.2s current transformers?
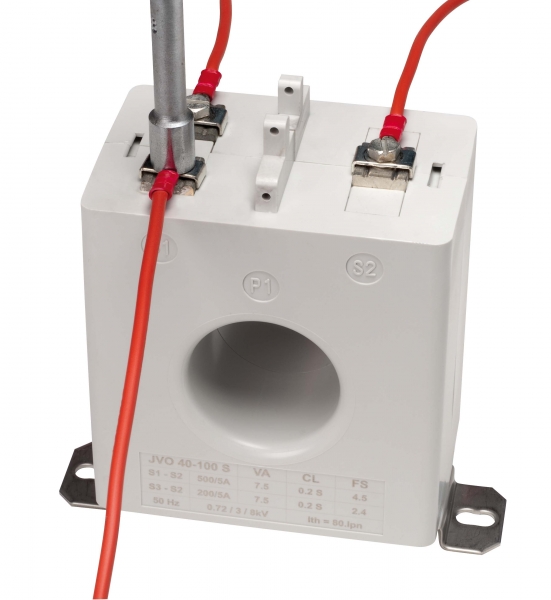 As an integral part of the measurement line for metering, the financial impact of a current transformer's accuracy class is considerable, so it must be taken into account when making your choice.
As an integral part of the measurement line for metering, the financial impact of a current transformer's accuracy class is considerable, so it must be taken into account when making your choice.
The right accuracy class to avoid losing money
For consumption of 12,000 MWh/year and a cost of 0.10 €/kWh
• Class 1 CT: ± 120,000 kWh or ± 12,000 €
• Class 0.5 CT: ± 60,000 kWh or ± 6,000 €
• Class 0.2s CT: ± 2,400 kWh or ± 2,400 €
(the calculation does not take into account the class of the measuring instrument or the line losses in the wiring network)
Supervising and managing electrical energy
Supervising your electrical network for better control at all times
 Deregulation and privatization of the energy market are causing energy suppliers in the public and private sectors to monitor the status of their electrical network. At different scales, both sectors face similar issues for proper energy use. Chauvin Arnoux Energy, a company in the Chauvin Arnoux Group, proposes its technological expertise with a range of products and systems which are accurate, reliable and long-lasting.
Deregulation and privatization of the energy market are causing energy suppliers in the public and private sectors to monitor the status of their electrical network. At different scales, both sectors face similar issues for proper energy use. Chauvin Arnoux Energy, a company in the Chauvin Arnoux Group, proposes its technological expertise with a range of products and systems which are accurate, reliable and long-lasting.
Nuclear, thermal or hydroelectric plants, wind or solar farms, new operators: the multiple, diverse locations and methods used for energy production are forcing historical energy producers to make sure that their network is suitably balanced. It is becoming increasingly necessary to measure at all points on the installation in order to maintain the right balance between production and consumption. Chauvin Arnoux Energy covers energy companies' specific, and standardized measurement and metering requirements with an offering of products operating in very severe environments:
On sites generating their own electrical energy (industrial sites, rail network), it is essential to protect, monitor and inspect the whole electrical network so that good-quality energy is constantly available. This necessarily calls for a real-time overview of the electrical parameters across the whole installation. Chauvin Arnoux Energy then proposes high-technology equipment:
Power monitors for supervising electrical networks
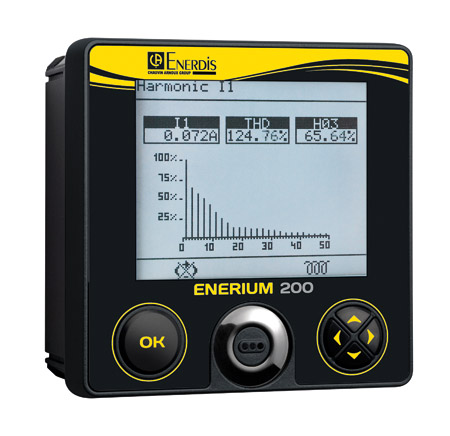
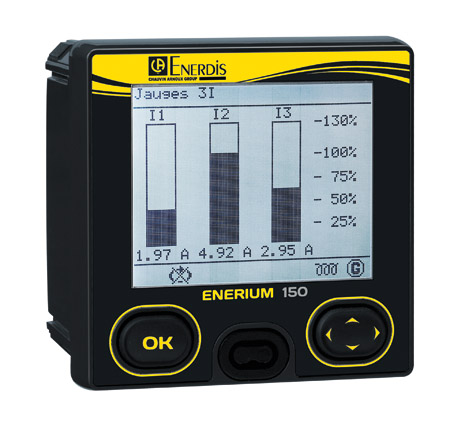
 A power monitor is a versatile element in the network which is installed on a feeder or inlet on the electrical switchboard in order to control, manage, operate and monitor the whole network by means of the following major functions:
A power monitor is a versatile element in the network which is installed on a feeder or inlet on the electrical switchboard in order to control, manage, operate and monitor the whole network by means of the following major functions:
Display
For maintenance and operation of the electrical network, the power monitor indicates the values of a wide range of network parameters, advantageously replacing a whole set of panel meters, transducers and switches. The gains for operators are not just financial (as soon as there is a power and/or energy management, the power monitor becomes more interesting in economic terms and considerably simplifies installation and wiring, as well as saving space on the switchboard or in the cabinet), but also technical because the power monitor will provide additional functions such as storage of the extreme values reached by the fundamental network parameters.
Capture and convert
With its numerous output possibilities, the power monitor becomes an energy meter (pulse output), a transducer (4...20 mA analogue outputs) or a digital sensor by means of a series link, so that you can access and process the data remotely. Lastly, thanks to its alarm outputs, supervision and maintenance of the electrical network are simplified by monitoring various parameters with regard to the thresholds programmed by the operator.
Inform
Intelligence: when associated with the internal clock, the power monitor's processor and memory enable it to offer recording functions. For operators, this means that the load curves of their network, the trends of the main parameters and the possibility of time/date-stamping events (alarms, outages, etc.) are available. To meet changing consumer demand, today's power monitors supervise the quality of the electricity supply: detection of voltage faults, calculation of the current in the neutral conductor, total harmonic distortion, etc.
Qualifying energy quality on the electrical network

Monitoring of the electrical network to limit operating losses by detailed mapping of the network and quickly identify any symptoms linked to energy quality.
Objectives
- Monitor and record very fast electrical phenomena at different points in the installation
- Capture electrical events lasting around one millisecond
- Analyze the recorded parameters and check the quality of the electrical energy flowing in the network
- Determine the origin of the malfunctions and establish whether their sources are located before or after the point of supply
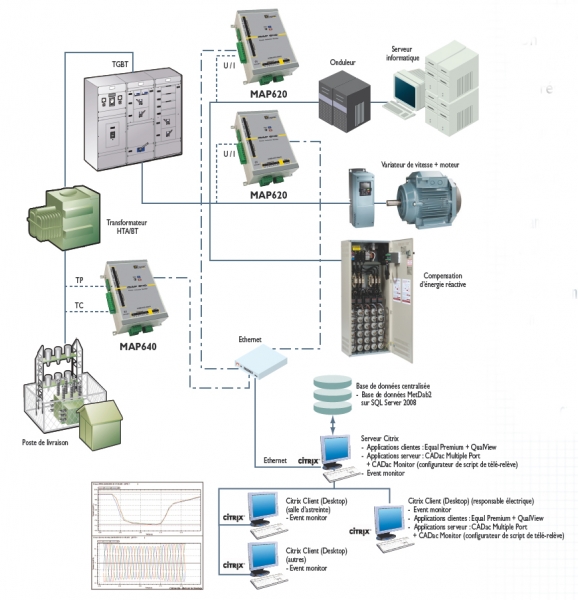
The Chauvin Arnoux Energy solution
Implementation of a system to measure the quality of the energy from several points in the electrical network by means of:
- permanent network quality analyzers compliant with IEC 61000-4-30 standard Class A: MAP 640 with capture of rapid transients - MAP 620
- software for automatic remote retrieval of the data from the equipment: E.Qual Premium Server
References
Nuclear plants:
CNPE EDF (France)
GUANGDONG NPP (China)
LINGAO NPP (China)
KHNP (Korea)
KOEBERG NPP (South Africa)
Transmission & Distribution:
RTE (France)
ERDF (France)
CIE (Côte d'Ivoire)
EDELNOR (Peru)
EDESUR and TRANSENER (Argentina)
EDL (Lebanon)
ELECTRABEL (Belgium)
ENEL (Italy)
SEC (Saudi Arabia)
NEK (Bulgaria)
ONE (Morocco)
PLN (Indonesia)
SONELGAZ (Algeria)
STEG (Tunisia)
SONABEL (Burkina Faso)
SENELEC (Senegal)
TNB (Malaysia)
UTE (Uruguay)
Chauvin Arnoux Metrix news
Chauvin Arnoux Metrix trade shows and events
Chauvin Arnoux Metrix press review
Chauvin Arnoux Metrix press releases
Chauvin Arnoux Metrix publications
Chauvin Arnoux Metrix training courses
Industry
CHAUVIN ARNOUX, the leading European manufacturer of measuring instruments, proposes all its know-how and technical facilities for your subcontracting work.
INDUSTRIAL SUBCONTRACTING
- PLASTIC INJECTION
- TOOLING
- SHEET-METAL CUTTING
- BAR TURNING - MACHINING
- PAINTING / PAD PRINTING
- WINDING
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
- ASSEMBLY
- PRINTING
- SHUNTS
An industrial partner serving your project - Our various industrial professions, integrated within the Group, are independent from one another but their complementary enables us to provide complete services, from manufacturing the spare parts through to the end product. This means we can offer:
• One-off subcontracting services in our various professions.
• Complete manufacturing of sub-assemblies or finished products.
The organization of our industrial resources is particularly suitable for small and medium-sized series, in compliance with your requirements in terms of monitoring and quality.
Total control of production quality
PLASTIC INJECTION - SHEET-METAL CUTTING TOOLS...
 PLASTIC INJECTION
PLASTIC INJECTION
Production of plastic parts and moulded parts in small and medium-sized series.
Moulding of all materials (PC, PA, ABS, PMMA, PET, POM, etc.)
PRODUCTION EQUIPMENT
Vertical and horizontal injection presses (12 to 360 tonnes).
 TOOLING
TOOLING
Design and production of moulds, cutting tools and various templates. Modification and maintenance of all types of tooling .
PRODUCTION EQUIPMENT
CAM, machining centre, wire electrical discharge machining and die-sinking
 SHEET-METAL CUTTING
SHEET-METAL CUTTING
Cutting and deep-drawing in small and medium-sized series.
Production of sheet-metal parts (instrument casings, front panels, etc.) by punching, folding and welding.
PRODUCTION EQUIPMENT
Digital punching machine, NC folder, Tig-Mig welding and spot welding equipment.
 BAR TURNING - MACHINING
BAR TURNING - MACHINING
All mechanical parts for the prototype up to medium-sized series.
Machining of all materials (steels, stainless steel, aluminium, plastics, copper and alloys).
PRODUCTION EQUIPMENT
NC lathes, machining centres, conventional machines.
 PAINTING / PAD PRINTING
PAINTING / PAD PRINTING
Liquid paint on all supports (metal and plastic).
Screen printing or pad printing of any markings (logo, text, drawing, etc.) with up to 4 colours in pad printing.
Laser engraving on metals and plastics, depending on compatibility.
 WINDING
WINDING
We can model and manufacture small wound elements needed for operation of your PCB, including current and voltage transformers, self-induction coils, coils, shunts, etc.
Finishing treatments are possible.
 PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
Production of single and double-sided printed circuit boards.
Wiring of printed circuit boards, surface-mount devices (SMDs) and insertion-mount components.
Automated optical weld testing and/or functional testing.
RoHS manufacturing
 ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY
Assembly of sub-assemblies and mechanical or electronic finished products.
 PRINTING
PRINTING
Printing of user manuals and other documents (colour or black and white) up to A3 format.
 A speciality: shunts
A speciality: shunts
Chauvin Arnoux Group, with it SMBO brand, benefits from acknowledged experience and know-how in the field of measurement shunts up to 4,000 A.
Thanks to its high-performance technological resources (machining centre and numerically controlled machines, bar turning of inserts), S.M.B.O. is constantly improving the manufacturing process and the quality of its products.
Certified ISO 9001 and ISO 14001.
Contact : soustraitance@chauvin-arnoux.com
Maintenance
Because each failure reduces productivity, maintenance teams set up plans for monitoring industrial processes. The aim of these plans is to identify and correct anomalies on installations by means of inspections and measurements before those anomalies reduce or halt production. Chauvin Arnoux measuring instruments are widely used both in regular preventive maintenance programmes and in corrective maintenance operations on installations or the machines connected to them.
Organization of maintenance
 By organizing regular preventive maintenance on an industrial process, it is possible to keep equipment or installations in perfect working order over the long term, while reducing the probability of failures.
By organizing regular preventive maintenance on an industrial process, it is possible to keep equipment or installations in perfect working order over the long term, while reducing the probability of failures.
The preventive maintenance plan thus includes systematic surveillance of the key elements involved in the industrial process.
This surveillance notably includes regular measurement and inspection operations. Analysis of the history of these data may also trigger conditional or predictive maintenance operations. For example, the detection of ageing or deterioration of certain parameters will trigger pre-failure maintenance, thus limiting the corrective maintenance necessary.
Electrical safety of the installation or machine
 To guarantee the safety of people and property with regard to electrical installations and the equipment connected to them, reference standards and/or regulations govern the testing of certain parameters on the installation, switchboards or machines.
To guarantee the safety of people and property with regard to electrical installations and the equipment connected to them, reference standards and/or regulations govern the testing of certain parameters on the installation, switchboards or machines.
To avoid interrupting the process, it is important to check the continuity of the protective conductor and the quality of the earth electrode, in order to ensure satisfactory equipotentiality between the installation reference and the machines connected to it. This avoids common-mode voltages, which may cause failures in the various sensitive electronic stages used to control and automate the process being powered.
NF C 15100 training
Find out more
Insulation of the conductors, in relation to one another and to the chassis, is essential in order to limit the leakage currents to earth which could influence the effective tripping thresholds, thus interrupting the process in progress. Lastly, by checking that the rated tripping values of the cut-off devices such as line circuit-breakers, RCDs and/or fuses are maintained, you can ensure that, in normal conditions, no untimely tripping will occur to interrupt the power supply.
In the context of systematic or conditional operations, the earthing is checked with earth testers using the 2P, 3P or 4P methods, or with loop testers, depending on the installation's configuration.
To ensure that the insulant meets the requirements, insulation resistance measurements are performed with insulation testers, also known as megohmmeters, at test voltages ranging from 1,000 V to 10/15 kV. This method is ideal for monitoring insulant ageing during the operation of equipment or an electrical installation so that it can be replaced if necessary.
To test the operation of RCD-type cut-off systems, RCD testers are used.
All these various measurements on an installation can be performed with multi-function installation testers. At the level of the machine and in addition to the tests listed above, a machine tester can be used for dielectric testing (flash testing) to check that the insulant withstands overvoltages. More specifically, an electrical appliance tester can be used to test the electrical safety of all the portable electrical equipment, machines and electrical control switchboards directly.
Multimeter clamps are very simple to use for measuring currents and leakage currents, particularly as their versatility means they can often be used for many other measurements as well.
More specific tests can also be performed, such as monitoring of the metallization and continuity of certain elements using a micro-ohmmeter, or monitoring of the transformer ratios with a ratiometer.
Thermal monitoring
 Because they are so quick to set up, no-contact temperature measurement systems have become essential tools for guaranteeing the safety of industrial production conditions. With infrared thermometers or thermographic cameras, it is now possible to detect thermal behaviour anomalies by relative or absolute measurements.
Because they are so quick to set up, no-contact temperature measurement systems have become essential tools for guaranteeing the safety of industrial production conditions. With infrared thermometers or thermographic cameras, it is now possible to detect thermal behaviour anomalies by relative or absolute measurements.
The purpose of the electrical tests is therefore to reveal any overheating on any infrastructure elements with loads, whatever the origins of the overheating (bad connections, overloads, phase unbalance, faulty contacts, undersizing, etc.)
In mechanical maintenance, this investigative method can be used to check for abnormal overheating (wear, bearing faults, insufficient lubrication, etc.).
Thermography training
Harmonic disturbances
 The widespread use of electronic power supplies in industrial processes is leading to an increase in harmonic disturbances on the electrical network which directly effects the quality of the energy distributed. In the short or medium term, these disturbances may eventually cause failures in all the electrical equipment connected to the network. Harmonic currents have negative effects on almost all the components of the electrical system by generating new dielectric, thermal and/or mechanical stresses.
The widespread use of electronic power supplies in industrial processes is leading to an increase in harmonic disturbances on the electrical network which directly effects the quality of the energy distributed. In the short or medium term, these disturbances may eventually cause failures in all the electrical equipment connected to the network. Harmonic currents have negative effects on almost all the components of the electrical system by generating new dielectric, thermal and/or mechanical stresses.
Electrical network analysers or harmonic analysers are then essential to quantify all the harmonics present on the network and to find a suitable solution.
Harmonics training
"Harmonics" Case Study
Maintenance of electronic control systems
 Maintenance of machines' electronic command and control systems requires measurements on the printed circuit boards where dynamic signals and different electrical references coexist side by side.
Maintenance of machines' electronic command and control systems requires measurements on the printed circuit boards where dynamic signals and different electrical references coexist side by side.
Portable oscilloscopes with isolated channels are the ideal tools for such tasks. With their multiple functions, they combine the possibilities of a digital oscilloscope, a multi-channel multimeter, a harmonic and FFT analyser and a logger. In the case of bus analyser oscilloscopes, they can also be used to check the transmission status of the signals exchanged by bus between the systems.
Link to SCOPIX site
Link to Handscope site
"Solenoid valve maintenance" Case Study
The various physical parameters in an industrial process
 Certain production or transformation tasks require control of parameters such as the pressure, temperature, flow rate, level, etc. These parameters govern the operation of the processes and are kept at predetermined levels by control and slaving techniques.
Certain production or transformation tasks require control of parameters such as the pressure, temperature, flow rate, level, etc. These parameters govern the operation of the processes and are kept at predetermined levels by control and slaving techniques.
Equipped with measurement and simulation functions (for current, voltage and temperature), portable calibrators are used during commissioning and maintenance of these measurement lines. Their uses include 4-20 mA or 0-10 V process loop tests and verification of temperature measurement lines.
In the context of pump maintenance, motor efficiency or compliance verification operations, various techniques may be used to measure the rotation or displacement of objects: stroboscopic method, contact tachometry or optical tachometry.